Module @relicprotocol/client
Relic Client SDK
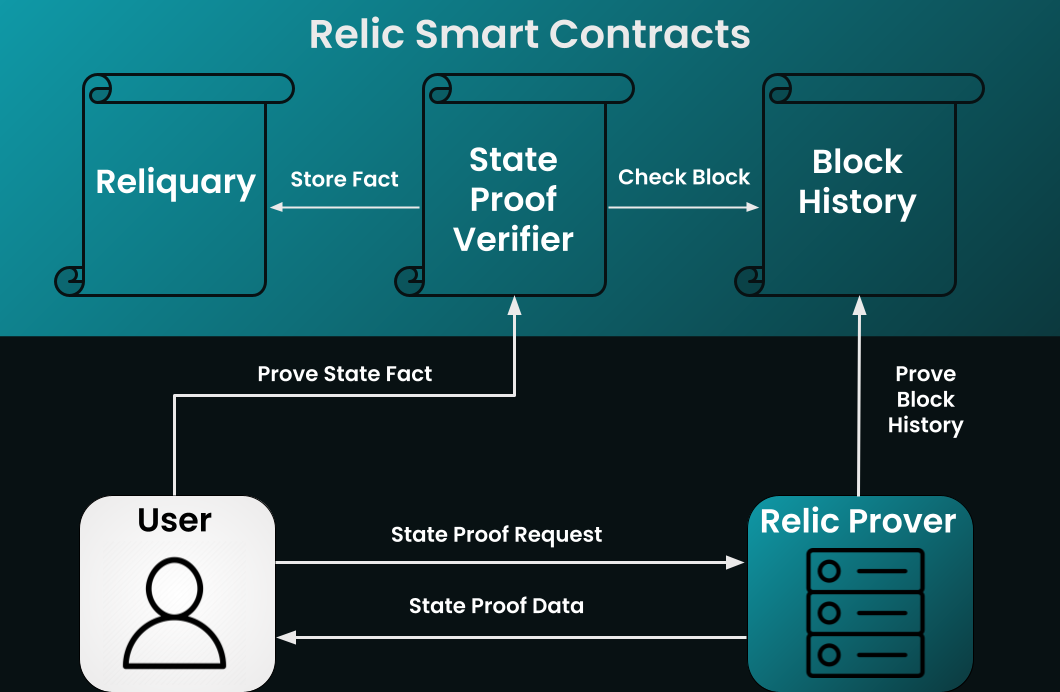
The client SDK is designed to simplify fetching proofs from the Relic Prover and generating transaction data to be submitted on-chain for verification.
Usage
Initializing RelicClient requires passing an ethers Provider. Providers can be created with an RPC url or by connecting to Metamask or another wallet extension.
import { AccountNotFound, RelicClient, utils, InfoType } from '@relicprotocol/client'
import { ethers } from 'ethers'
async function main() {
// Note: you could also get the provider from a browser wallet extension
const provider = new ethers.providers.JsonRpcProvider('[RPC URL here]')
const signer = await provider.getSigner()
const relic = await RelicClient.fromProvider(provider)
// prove an account's birth certificate
const account = '0xd8dA6BF26964aF9D7eEd9e03E53415D37aA96045' // vitalik.eth
const bcTx = await relic.birthCertificateProver.prove({ account })
console.log(await provider.estimateGas(bcTx))
// use the transaction data...
// to send the proof transaction as is:
// let tx = await signer.sendTransaction(bcTx)
// await tx.wait()
// prove an account's code hash
// note: other account data fields can be proven by changing the |info| param
const aiTx = await relic.accountInfoProver.prove(
{ block, account, info: InfoType.CodeHash }
)
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await provider.estimateGas(aiTx)
// prove a storage slot's value, in this case WETH.balanceOf(account)
const blockNum = 15000000
const wethAddr = '0xC02aaA39b223FE8D0A0e5C4F27eAD9083C756Cc2' // WETH
const slot = utils.mapElemSlot(3, account) // calculate balanceOf(account) slot
// you can optionally specify the expected slot value, to ensure the slot is correct
// we'll compute this by calling balanceOf(account) at the target block
const contract = new ethers.Contract(
wethAddr,
['function balanceOf(address) external view returns (uint256)'],
provider
)
const expected = await contract.balanceOf(account, { blockTag: blockNum })
// expected is optional parameter
const ssTx = await relic.storageSlotProver.prove({
block: blockNum,
account: wethAddr,
slot,
expected,
})
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await provider.estimateGas(ssTx))
// You can also prove multiple storage slots in one call to save gas
const ZERO_ADDR = '0x' + '0'.repeat(40)
const slot2 = utils.mapElemSlot(3, ZERO_ADDR) // calculate balanceOf(0x000..00) slot
const expected2 = await contract.balanceOf(ZERO_ADDR, { blockTag: blockNum })
// prove two storage slots from the same account simultaneously
const mssTx = await relic.multiStorageSlotProver.prove({
block: blockNum,
account: wethAddr,
slots: [slot, slot2],
expected: [expected, expected2],
})
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await provider.estimateGas(mssTx))
// prove the storage root an account in a particular block,
// potentially making slot proofs in that block much cheaper
const asTx = await relic.accountStorageProver.prove({
block: 15000000,
account: wethAddr,
})
console.log(await provider.estimateGas(asTx))
// once the above transaction is confirmed, you can use cheap cached storage
// slot proofs for that (account, block)
const cssTx = await relic.cachedStorageSlotProver.prove({
block: blockNum,
account: wethAddr,
slot,
expected,
})
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await provider.estimateGas(cssTx))
// Now let's prove some ephemeral facts; a block header proof and a log proof
// NOTE: you probably don't want to prove these facts without using proveEphemeral,
// because storing these large facts on-chain costs a lot of gas
// Your contract which implements IRelicReceiver
// Consider using the RelicReceiver base contract in the solidity SDK
const receiver = '0x...'
// prove a historical block header is valid
const bhTx = await relic.blockHeaderProver.proveEphemeral(
{
initiator: await signer.getAddress(),
receiver,
gasLimit: 50000, // 50000 gas is enough for our receiver callback, be sure to check yours!
},
{ block: 15000000 }
)
console.log(await signer.estimateGas(bhTx))
// get BAYC mint events
// NOTE: this may be very slow if your RPC provider doesn't index logs well
const logs = await provider.getLogs({
address: '0xBC4CA0EdA7647A8aB7C2061c2E118A18a936f13D', // BAYC contract
topics: [
'0xddf252ad1be2c89b69c2b068fc378daa952ba7f163c4a11628f55a4df523b3ef', // Transfer event
'0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000', // from == address(0)
],
fromBlock: 0,
})
// prove the first BAYC mint log
const logTx = await relic.logProver.proveEphemeral(
{
initiator: await signer.getAddress(),
receiver,
gasLimit: 50000,
},
logs[0]
)
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await signer.estimateGas(logTx))
// prove the first withdrawal
const withdrawalTx = await relic.withdrawalProver.prove({
block: 17034871,
idx: 0,
})
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await signer.estimateGas(withdrawalTx))
// prove a transaction was included
const receipt = await provider.getTransactionReceipt(logs[0].transactionHash)
const txTx = await relic.transactionProver.prove(receipt)
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await signer.estimateGas(txTx))
// prove a beacon chain withdrawal occured
const withdrawalTx = await relic.withdrawalProver.prove(
{ block: 17034871, idx: 0 } // first withdrawal in the first shapella block
)
// use the transaction data...
console.log(await signer.estimateGas(withdrawalTx))
// demonstrate error handling
try {
const randomAddr = ethers.utils.hexlify(ethers.utils.randomBytes(20))
await relic.birthCertificateProver.prove({ account: randomAddr })
} catch (error: any) {
if (!(error instanceof AccountNotFound)) throw error
// handle account not found
}
}
main()
Index
Namespaces
Enumerations
Classes
Account